
A unique series of Books and Apps for the Surveying, Engineering, GIS Professionals and aspiring Students.



Go back to previous screen
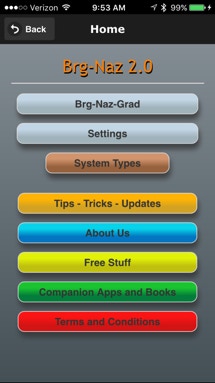
Bearing - Azimuth - Grad Calculations
Set default settings
System Types
Online Tips, Tricks and Updates
About the author/programmer
Online Free Stuff
Other Apps and Books
Terms and Conditions



Go back to previous screen

Input Quick Reference



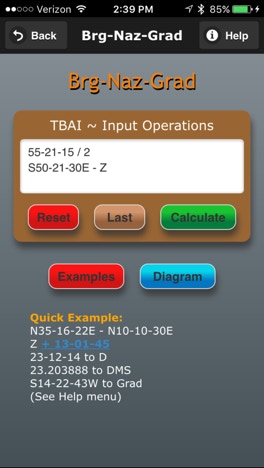
Text Based Artificial Intelligence (TBAI) interface.
A user interface using simple text to input the bearing, azimuth or grad operations.
App help menu
Reset: Clears and resets the TBAI
Last: Recalls that last data input
Calculate: The TBAI is parsed and calculates the bearing, azimuth or grad operations.
Examples
Angle and Bearing diagram
Enter each operation on a separate line in the TBAI as follows:
[argument1] [space] [operator] [space] [argument2]
Note: Use only ONE space between the arguments and operator or an error will occur.
The TBAI will recognize the following operations, operators and conversions:
Conversions:
DMS to D
D to DMS
Brg to Naz
Brg to Saz
Brg to Grad
Naz to Brg
Naz to Saz
Naz to Grad
Saz to Brg
Saz to Naz
Saz to Grad
Grad to Brg
Grad to Naz
Grad to Saz
Operators:
to [Conversion]
- [Subtraction]
+ [Addition]
x [Multiplication]
/ [Division]
Operations:
Brg - Brg
Brg - Angle
Brg + Angle
Angle - Angle
Angle + Angle
Angle x #
Angle / #
The following is an example of a multiline angle and bearing operation:

The first line is an angle divided by 2.
The second line is a bearing - the result of the first line.
The third line is a bearing minus a bearing.
The fourth line is a bearing - cardinal direction.
The fifth line is the result of the fourth line - an angle.
Tap the ‘Calculate’ button to have the TBAI parse the input data and calculate each line in sequence.
Note: To use the result of the previous line enter a ‘Z’. Z is updated with the result for each line as temporary storage.
The TBAI will recognize the following directions and angles:
Bearings: (Ndd-mm-ddE, Ndd.dddddE) for all four quadrants
North Azimuth: (NAZdd-mm-ss, NAZdd.ddddd)
South Azimuth: (SAZdd-mm-ss, SAZdd.ddddd)
Cardinal: N, North, S, South, E, East, W, West)
Grad a.k.a. Gon (Gxx.xxxxx)
Angle: (dd-mm-ss, dd.ddddd)
When subtracting bearings or angles the operation is performed in a counter-clockwise direction and adding bearings or angles the operation is performed in a clockwise direction.
Precede any line with an apostrophe to ignore that line. i.e. ’45-44-22 - 3-15-34
Error Message:
“Line skipped: Operation unknown!”
The entry as shown between the brackets [xxxx] is not formatted correctly. Check the arguments and operator to insure that they are correct. Note: There should be only ONE space between the arguments.

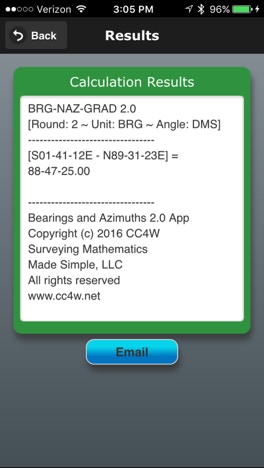
The Results page is as follows:
The default settings are displayed.
[Round: 5 ~ Unit: BRG ~ Angle: DMS]
See below to change the default settings.
The operation is shown in the [brackets] followed by the result of the operation.
Angle / 2
[55-21-15 / 2] = 27-40-37.50000
To use the result of the previous line enter the letter Z.
[s50-21-30e - z] which is [s50-21-30e - 27-40-37.5000] = S78-2-7.50000E



Go back to previous screen

Input Quick Reference





Reset: Clears and resets the TBAI
Last: Recalls that last data input
Save: The TBAI will save the default settings.
Examples of value settings.
Required codes and values.
Text Based Artificial Intelligence (TBAI) interface.
A user interface using simple text to input the defaults for Rounding, Unit and Angle format.
App help menu
Enter in the TBAI the three required codes. The TBAI needs these codes to set the default values needed for the Brg-Naz-Grad module.
The three required codes are Round, Unit and Angle. Each code name is followed by an “=“ sign then the appropriate value as such: (CODE = VALUE)
Round = 5 (This is for the number of decimal places to show.)
Unit = BRG (Values can be BRG, NAZ, SAZ, GRAD)
Angle = DMS (Values can be DMS or D)

The following examples are a comparison between the HP calculator and the Brg-Naz 2.0 app. The App is much more efficient than the calculator when working with bearings and angles.
If an error is made on the calculator, you have to start all over. On the App you go back, fix the entry and re-calculate. You do no have to start over.
EXAMPLE 1: Solve for Local Tangent Bearing
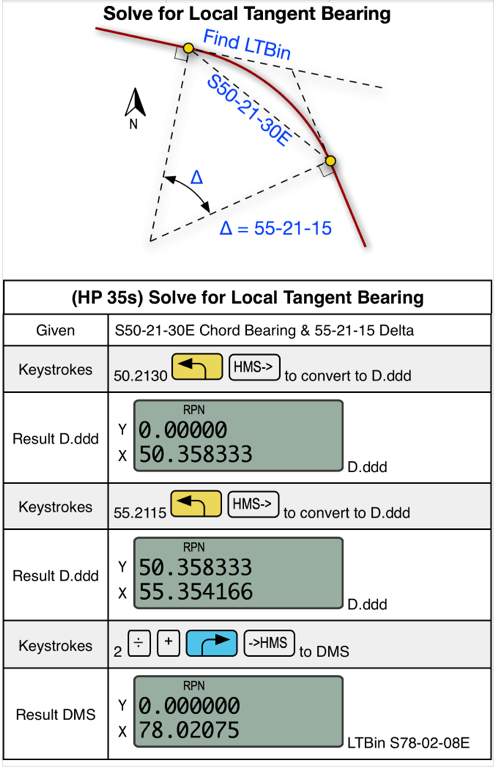
Not counting the digit entry.
Calculator: 9 steps
Brg-Naz 2.0: 1 step

EXAMPLE 2: Find Angle between Section Lines
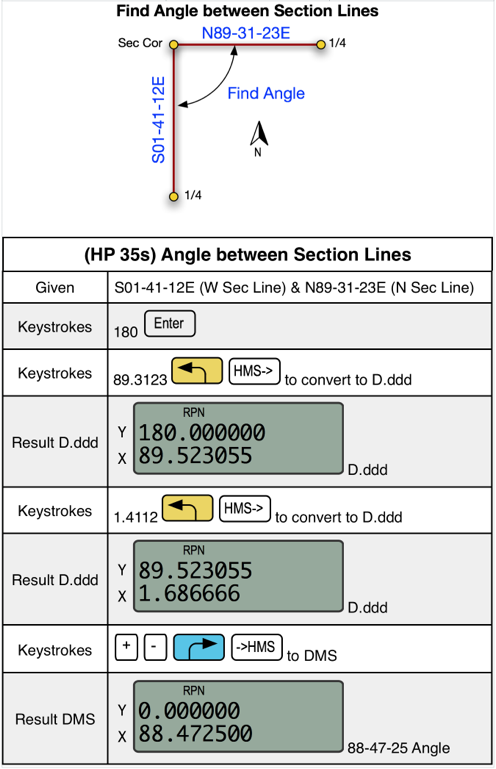
Not counting the digit entry.
Calculator: 9 steps
Brg-Naz 2.0: 1 step

EXAMPLE 3: Compare Record Delta to Calculated Delta given LTBin, LTBout & Delta (R).
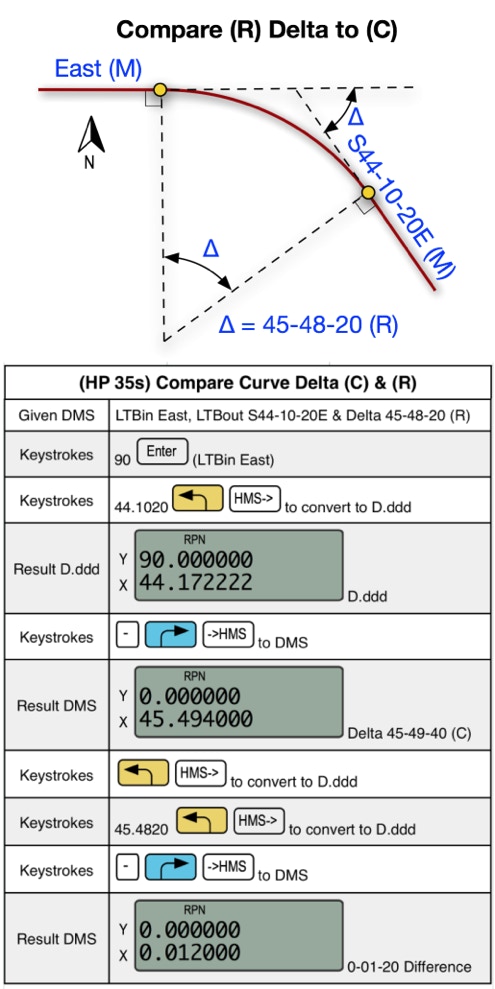

Not counting the digit entry.
Calculator: 13 steps
Brg-Naz 2.0: 1 step
Copyright © 2001-2018 CC4W All rights reserved
Website designed by Creative Computing 4 Windows










